Small motors convert electric energy into mechanical energy. Depending on the power supply, small motors are an efficient size and incredibly pleasant and practical to operate. Small electric motors are dependable equipment; however, as simple devices, it may be faster to replace a motor than to fix it. Read More…
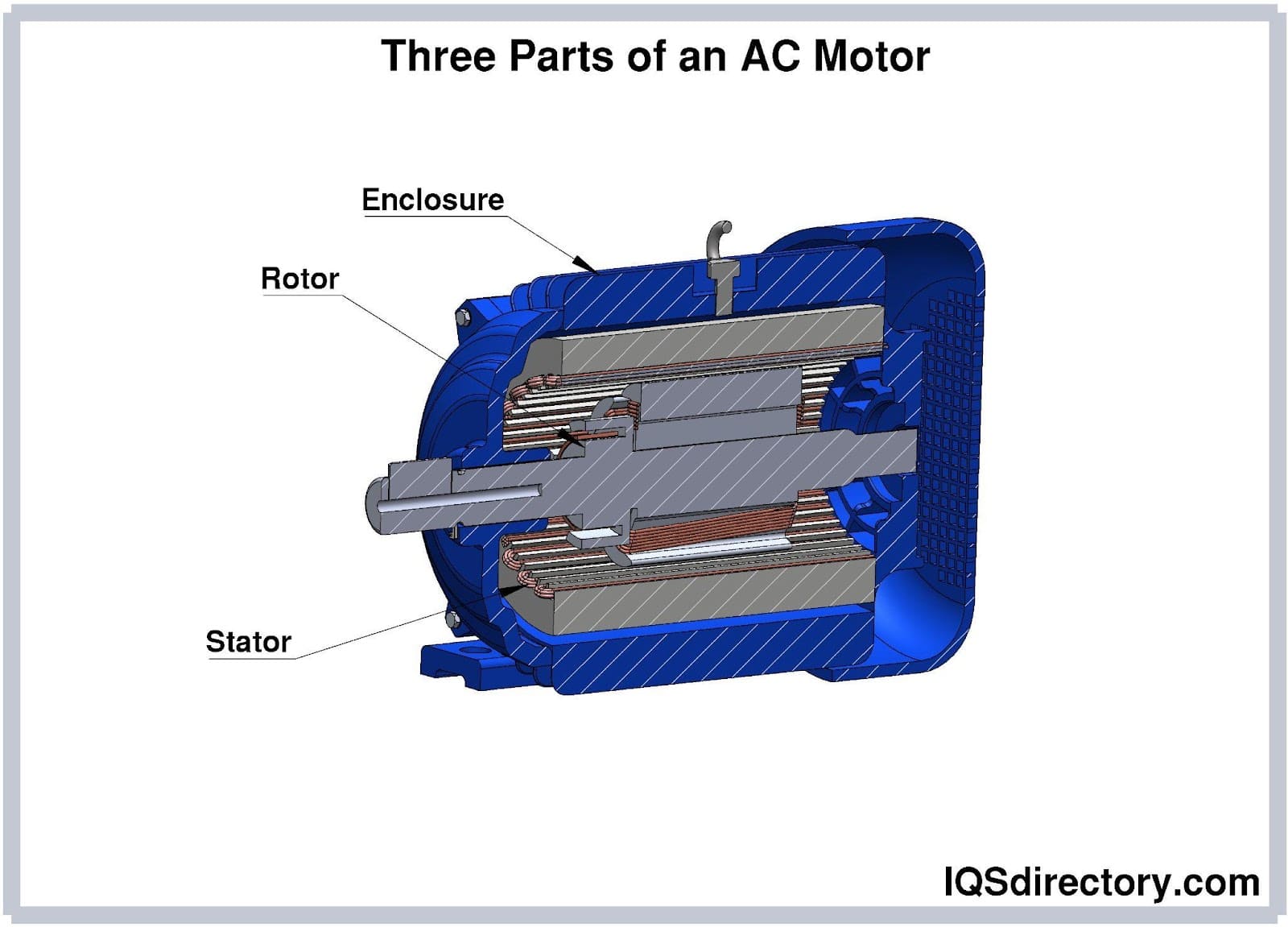
At AutomationDirect.com, we specialize in providing a wide range of electric motors and electronic enclosures to meet our customers' diverse needs. Our commitment to excellence drives us to offer top-quality products that deliver superior performance and reliability. With our extensive selection of electric motors, ranging from AC motors to DC motors and everything in between, we empower...
When reliability and power are a must, the universal motors you find at ElectroCraft can operate with high efficiency, low voltage, and at a low cost. Applications that our universal electric motors serve include robotics, packaging, automotive, and medical equipment. Electric motor products include the CompletePower™ Plus Universal Drive, complete with a user-friendly configurable interface....
Carter Motor has over 70 years of experience in quality electric motor manufacturing. Some of the motors manufactured include, AC universal motors, small motors, DC universal motors, DC permanent magnet motors, DC shunt wound motors and gearmotors, along with many others. All of our products are designed and assembled in the United States by our dedicated team of engineers.
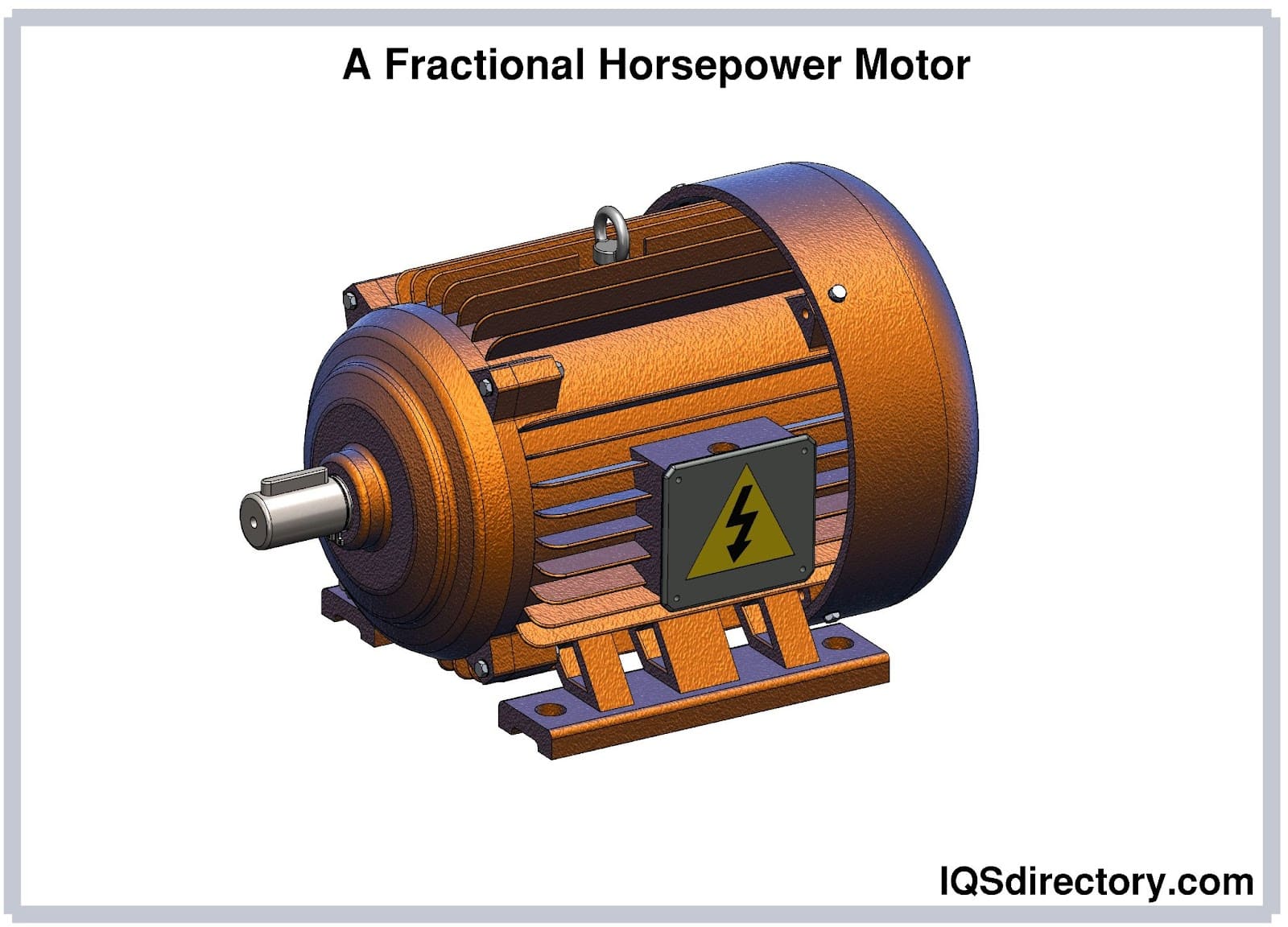
When you choose Composite Motors, you gain access to a reliable and forward-thinking partner in the realm of fractional horsepower motors. Our products are designed to endure, ensuring that your systems operate at their best for years to come. Join us in embracing the power of innovation and quality, as we continue to shape the future of fractional horsepower motors together.
More Small Motor Manufacturers
Operating Concept for Small Motors
Small motors, also known as miniature electric motors or fractional horsepower motors, utilize a powerful magnet to create rotational force and convert electrical energy into mechanical rotational motion. This fundamental process is essential in a wide range of devices that require compact, energy-efficient actuation. The orientation and direction of the motor’s spin can be easily adjusted by reversing the polarity of the battery leads, offering flexible integration into electronic circuits and machinery. Small motors are commonly manufactured as either single-phase or three-phase motors, each serving different operational needs and electrical configurations. Their affordability, reliability, and straightforward maintenance have made small motors an essential component in consumer electronics, industrial automation, medical devices, robotics, and countless other applications.

Wondering how small electric motors work in your specific application or what makes a DC motor ideal for miniature tasks? Learn more about small motor applications and how to select the right type for your project.
Types of Small Motors
Small motors enhance performance, precision, and control in a diverse array of motion control systems. Selecting the correct type of small motor is crucial for optimizing efficiency, cost, and operational reliability. Here, we explore popular varieties and their unique advantages:
Small Brushless DC Motors
Brushless DC (BLDC) small motors are recognized for their outstanding speed control, high efficiency, and longer operating lifespans compared to traditional brushed motors. The design of brushless motors eliminates mechanical brushes and commutators, reducing wear and the need for maintenance. Their high velocity and torque ratings make brushless DC motors ideal for demanding applications such as drones, electric vehicles, medical devices, robotics, and high-precision industrial equipment.
There are two main subtypes of brushless motors: slotless and slotted. Slotless small motors use an ironless stator with tube-shaped coils, giving them superior smoothness and reduced cogging torque—perfect for applications requiring quiet operation and high positional accuracy, such as laboratory automation and surgical robots. Slotted small motors, by contrast, offer greater torque density and are preferred in power-dense, rugged environments.
Additionally, brushless small motors are frequently employed in environments that demand sterilization or cleanroom compliance, such as medical imaging equipment, surgical tools, and diagnostic devices. Their precise control and minimal particle generation make them a top choice in the healthcare and biotechnology industries.
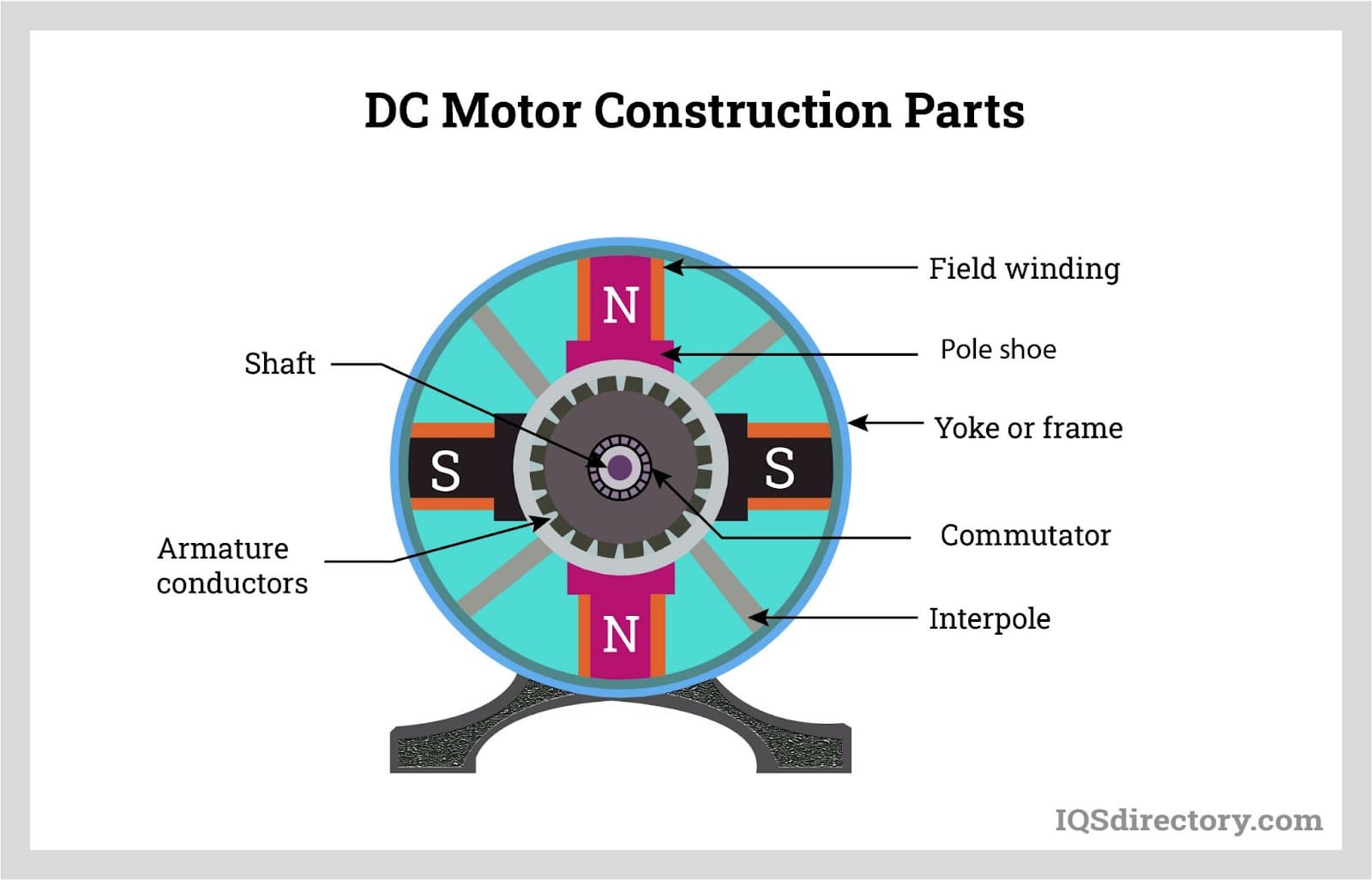
Brushed DC Motors
Brushed DC motors, sometimes referred to as conventional DC motors, remain a staple in both large and small electronic devices due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. They offer several advantages:
- Low friction and minimal starting voltage—well-suited for battery-powered devices.
- Negligible iron losses—increases energy efficiency.
- Linear torque-speed relationship—ensures predictable performance.
- Excellent thermal dissipation—helps prevent overheating in confined spaces.
- Good speed-to-torque performance—delivers reliable operation in compact form factors.
Brushed DC motors are widely used in consumer electronics (such as toys, small appliances, and automotive actuators), as well as in industrial automation where cost and simplicity are priorities. Their straightforward design makes them easy to control, repair, and integrate into both new and legacy systems.
Motors with Linear Steps
Linear stepper motors, or linear actuators, produce direct translational motion rather than rotation. These specialized small motors are cost-effective solutions for applications demanding reliable, controlled linear movement. By converting electrical pulses into incremental steps of movement, linear stepper motors provide precise positioning and repeatability—essential for tasks such as 3D printing, CNC machinery, laboratory automation, and semiconductor manufacturing.
The simplified design of linear motors, often combined with ball bearings, enhances load handling capabilities and significantly extends service life. Digital control via microprocessors or PLCs enables real-time adjustments, supporting highly automated production lines and customizable workflows. If you need a small motor for accurate, programmable linear movement, linear stepper motors are a compelling choice.

Micro Stepper Motors
Micro stepper motors, also called tiny step motors or micro-stepping motors, are compact brushless DC motors designed to divide full rotations into precisely controlled, equal steps. Their incremental movement makes them ideal for applications such as camera lens control, miniature robotics, wearable devices, and instrumentation requiring high precision and repeatability.
Unlike traditional motors, micro stepper motors can hold or move to specific positions without the need for feedback sensors (a technology known as open loop control). This reduces complexity and cost while delivering reliable performance in space-constrained environments. To maximize efficiency and avoid missed steps, it’s important to correctly scale the motor’s torque and speed for the intended application.
Interested in integrating micro stepper motors into your product design? Find stepper motor manufacturers and compare technical specifications to ensure compatibility with your control system.

Other Small Motor Types
- Can Stack Motors: Economical stepper motors suitable for light-load applications like printers and vending machines.
- Surgical Motors: Designed for high precision and sterilizability in medical instruments and devices.
- Ultra EC Motors: High-efficiency, compact motors engineered for demanding tasks in lab automation and critical medical equipment.
Applications of Small Motors
Small motors serve as the backbone of countless modern devices and systems, powering everything from consumer gadgets to industrial automation solutions. Below, we outline the industries and use cases that benefit most from the versatility and performance of small electric motors:
- Textile and Footwear Manufacturing: Small motors drive sewing machines, embroidery equipment, and automation modules.
- Timber Applications: Used in saws, conveyors, and automated wood-processing machinery.
- Plastic and Rubber Manufacturing: Enable precise material handling, extruders, and injection molding machines.
- Toys and Watches: Miniature motors provide the motion in electronic toys, quartz watches, and model vehicles.
- Printing Industry: Power rollers, feeders, and actuators for high-speed, accurate printing processes.
- Nautical Purposes: Drive small pumps, winches, and control surfaces on boats and marine devices.
- Bottling and Packaging: Operate conveyors, labeling systems, and capping mechanisms for bottling lines.
- Electromechanical and Motorized Industries: Used in actuators, valves, and automation modules for process control.
- Medical Operations: Essential in surgical handpieces, infusion pumps, imaging devices, and diagnostic analyzers.
- Consumer Products: Found in hairdryers, coffee makers, robotic vacuum cleaners, CD/DVD drives, and hard disk drives.
- Fans and Pumps: Provide airflow, cooling, and fluid movement in HVAC, appliances, and industrial systems.
- Spindle Drives: Enable variable-speed operation for machine tools, laboratory mixers, and automated assembly lines.
- Automotive Systems: Control power windows, seat adjustments, mirrors, and HVAC actuators in vehicles.
- Smart Home Devices: Power actuators in home automation systems, such as smart blinds, locks, and security cameras.
- Robotics and Automation: Deliver the precise motion control required for industrial robots, pick-and-place machines, and collaborative robots (cobots).
Curious about which small motor is best for your industry or application? Ask yourself:
- What is the required torque, speed, and duty cycle for your process?
- Will the environment demand special features such as waterproofing, sterilizability, or explosion-proof ratings?
- Is positional accuracy or smooth operation critical to the success of your project?
- Do you need open- or closed-loop control for feedback and automation?
Benefits of Using Small Motors
The widespread adoption of small motors is rooted in their significant advantages across multiple sectors. Here are some of the key benefits that make small motors indispensable in modern engineering and design:
- Compact Size: Fits easily into space-constrained devices, enabling miniaturization of products.
- High Efficiency: Converts electrical power to mechanical motion with minimal losses, reducing energy consumption.
- Precise Control: Offers fine adjustment of speed, position, and torque, vital for automation and robotics.
- Lightweight: Reduces overall system weight, which is essential for portable and wearable devices.
- Cost-Effective: Affordable to manufacture, purchase, and maintain, making them accessible for mass production.
- Low Noise and Vibration: Brushless and micro stepper motors deliver quiet operation for sensitive environments.
- Versatile Power Options: Available in AC, DC, and battery-powered variants to suit diverse electrical systems.
- Customization: Easily tailored to specific torque, size, voltage, and control requirements for niche applications.
- Reliability: Proven operational durability in harsh and continuous-use environments.
Want to maximize the benefits of small motors in your application? Contact a small motor expert for design consultation or request a custom quote based on your specifications.
Decision Factors When Buying Small Motors
Selecting the right small motor for your application requires careful analysis of requirements, performance characteristics, and environmental constraints. Here’s a comprehensive guide to the main factors you should consider when evaluating and purchasing small motors:
- Operational Mode: Will the motor operate continuously, intermittently, or in short bursts? Duty cycle impacts motor selection and longevity.
- Voltage and Power Ratings: Ensure compatibility with your power supply, battery, or onboard electronics.
- Torque and Speed Requirements: Define the load and performance needs for optimal sizing and efficiency.
- Physical Dimensions and Weight: Space limitations may dictate maximum motor size and mounting options.
- Control System: Do you need analog, digital, open loop, or closed loop control for precise actuation?
- Environmental Considerations: Consider temperature, humidity, dust, vibration, and exposure to chemicals or moisture.
- Noise and Vibration: Some applications—like medical or laboratory equipment—require ultra-quiet operation.
- Regulatory and Safety Standards: Is compliance with NEMA, IEC, UL, or other standards required?
- Customization: Do you require special shaft lengths, gears, or mounting brackets?
- Lifecycle and Maintenance: Estimate expected service intervals and replacement part availability.
Even if the horsepower exceeds one unit, a motor may still be classified as a fractional horsepower motor based on frame size and application. To determine NEMA motor compliance, the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) has established frame size standards (such as 42, 48, or 56 frames), which dictate compatibility and interchangeability in industrial settings.
Need help with sizing, standards, or compliance? Explore: NEMA standards for small motors to learn more about industrial requirements and best practices.
How to Choose the Right Small Motor Supplier
Finding a reliable small motor supplier is crucial for ensuring quality, technical support, and on-time delivery. Here are key steps and search prompts to help you identify, evaluate, and select the best supplier for your needs:
- Research and Compare: Use our directory of small motor suppliers to review company profiles, specializations, and capabilities.
- Assess Technical Expertise: Does the supplier offer engineering support, customization, or prototyping for your application?
- Check Certifications: Confirm compliance with industry standards such as ISO 9001, UL, NEMA, and RoHS.
- Review Customer References: Ask for case studies or testimonials in your industry segment.
- Evaluate Lead Times: Consider the supplier’s inventory, manufacturing capacity, and delivery schedules.
- Request Quotes and Samples: Use our RFQ form to contact multiple suppliers with your requirements and compare pricing and delivery options.
- After-Sales Support: Ensure the supplier offers technical support, warranty, and easy access to replacement parts.
Our platform allows you to preview each small motor business website using our proprietary website previewer—making it easy to gauge their expertise, product range, and value-added services. Use the simple RFQ (Request for Quote) form to contact several suppliers at once, ensuring you get the best combination of price, lead time, and technical support.
Ready to start your search? Find a qualified small motor supplier or request a quote for your specific needs today.
Frequently Asked Questions about Small Motors
What is a fractional horsepower motor? A fractional horsepower (FHP) motor is an electric motor rated below one horsepower (746 watts). These motors are widely used in light-duty applications where space and power are limited.
How do I determine the best small motor for my application? Consider the required torque, speed, voltage, control method, and physical form factor. Consult datasheets, application notes, and supplier recommendations for optimal sizing.
Can small motors be customized? Yes, many manufacturers offer customized winding, shaft, mounting, and control options to meet unique application requirements. Contact suppliers directly for design consultations.
What maintenance do small motors require? Maintenance varies by type. Brushless small motors require minimal service, while brushed motors may need periodic brush replacement. Always follow manufacturer guidelines for lubrication and inspection.
Conclusion: Powering Innovation with Small Motors
Small motors are at the heart of innovation in countless industries, from consumer electronics and smart devices to advanced medical equipment, laboratory automation, and industrial robotics. With a deep understanding of small motor types, applications, benefits, and selection criteria, you can confidently choose the ideal solution for your project or manufacturing process. Whether you need a high-precision brushless DC motor, a cost-effective brushed DC motor, or a specialized micro stepper or linear actuator, today’s small motors deliver unmatched performance, reliability, and value.
Ready to find the right motor for your needs? request a custom quote for expert assistance.





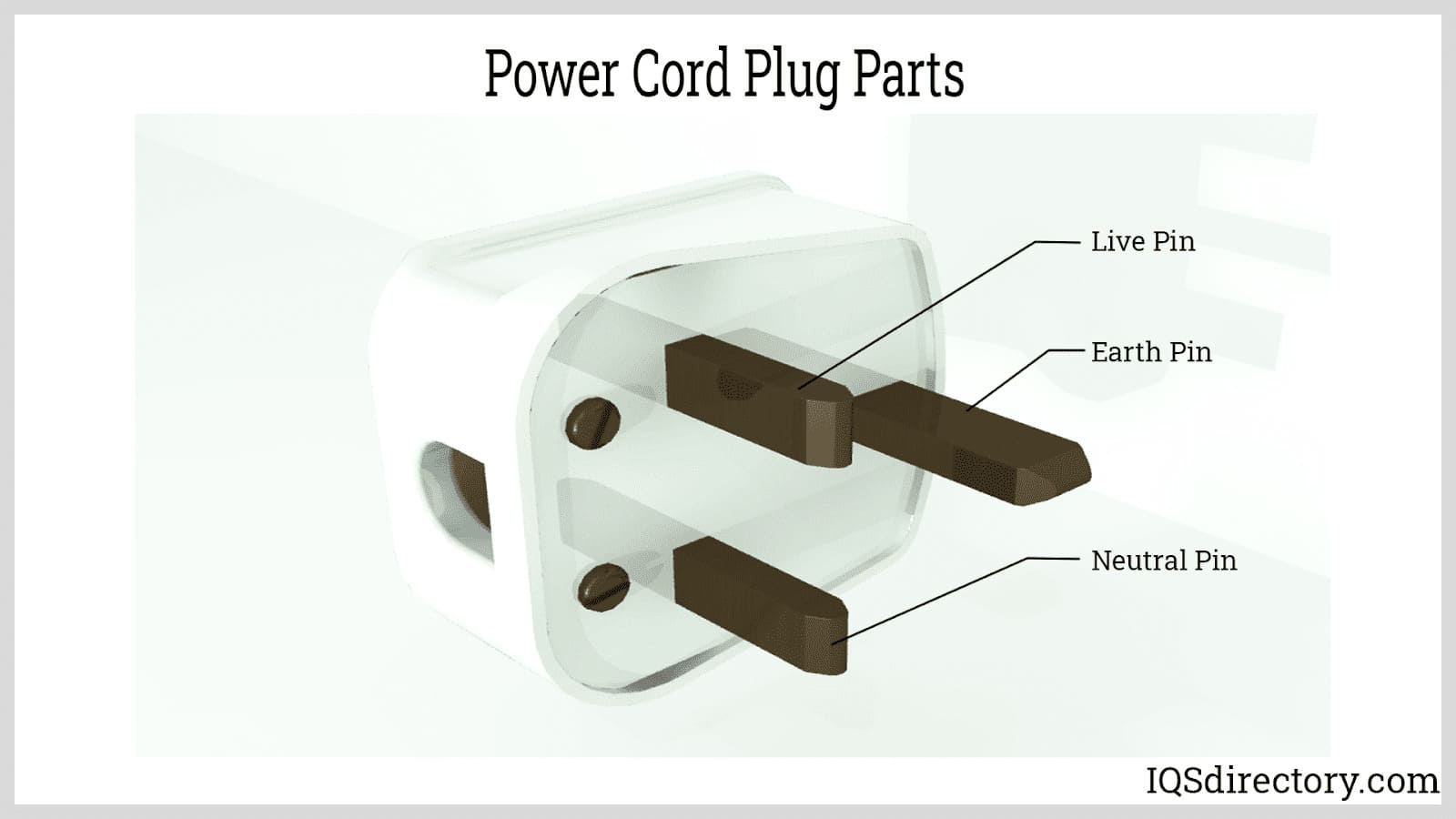
 Air Cylinders
Air Cylinders Assembly Machinery
Assembly Machinery Ball Bearings
Ball Bearings Electric Motors
Electric Motors Fractional Horsepower Motors
Fractional Horsepower Motors Friction Materials
Friction Materials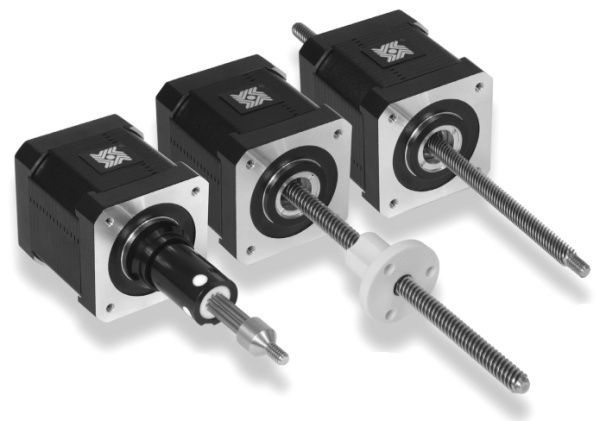 Linear Actuators
Linear Actuators Linear Bearings
Linear Bearings Linear Slides
Linear Slides Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services