A universal motor is a special motor that runs on either single-phase AC (alternating current) power or a DC (direct current) supply. These motors typically have series-wound armatures and field windings, which result in strong starting torque. Most universal motors are directly integrated into the machinery designed to power. Most universal motors are designed to work at speeds greater than 3500 RPM. They run slower when powered by an AC source than when powered by a DC supply of the same voltage because of a higher voltage drop that occurs through AC supplies. Read More…
At AutomationDirect.com, we specialize in providing a wide range of electric motors and electronic enclosures to meet our customers' diverse needs. Our commitment to excellence drives us to offer top-quality products that deliver superior performance and reliability. With our extensive selection of electric motors, ranging from AC motors to DC motors and everything in between, we empower...
When reliability and power are a must, the universal motors you find at ElectroCraft can operate with high efficiency, low voltage, and at a low cost. Applications that our universal electric motors serve include robotics, packaging, automotive, and medical equipment. Electric motor products include the CompletePower™ Plus Universal Drive, complete with a user-friendly configurable interface....
Carter Motor has over 70 years of experience in quality electric motor manufacturing. Some of the motors manufactured include, AC universal motors, small motors, DC universal motors, DC permanent magnet motors, DC shunt wound motors and gearmotors, along with many others. All of our products are designed and assembled in the United States by our dedicated team of engineers.
When you choose Composite Motors, you gain access to a reliable and forward-thinking partner in the realm of fractional horsepower motors. Our products are designed to endure, ensuring that your systems operate at their best for years to come. Join us in embracing the power of innovation and quality, as we continue to shape the future of fractional horsepower motors together.
More Universal Motor Manufacturers
Universal motors come in two different categories—compensated and uncompensated. Compensated universal motors use additional, scattered-field winding to help reduce power distortion when operating on AC power, making them more suitable for high-performance and high-speed applications. Understanding the differences between compensated and uncompensated types is crucial for engineers, OEMs, and buyers looking to select the most appropriate universal motor for their specific use case in the electric motor industry.
What Is a Universal Motor? Key Features & Functionality
A universal motor is a type of electric motor that can operate on either single-phase AC (alternating current) or DC (direct current) power supply. Its flexible compatibility makes it an ideal choice for a wide range of portable power tools, household appliances, and industrial equipment. Universal motors are characterized by their high starting torque, compact design, and ability to run at very high speeds—often up to 25,000 RPM. This versatility gives universal motors a vital role in applications such as vacuum cleaners, power drills, sewing machines, and kitchen appliances.
Are you evaluating universal motor applications for your product or project? Explore our applications section below to learn where universal motors excel and how they compare to other types of fractional horsepower motors.
Universal Motor Mechanism
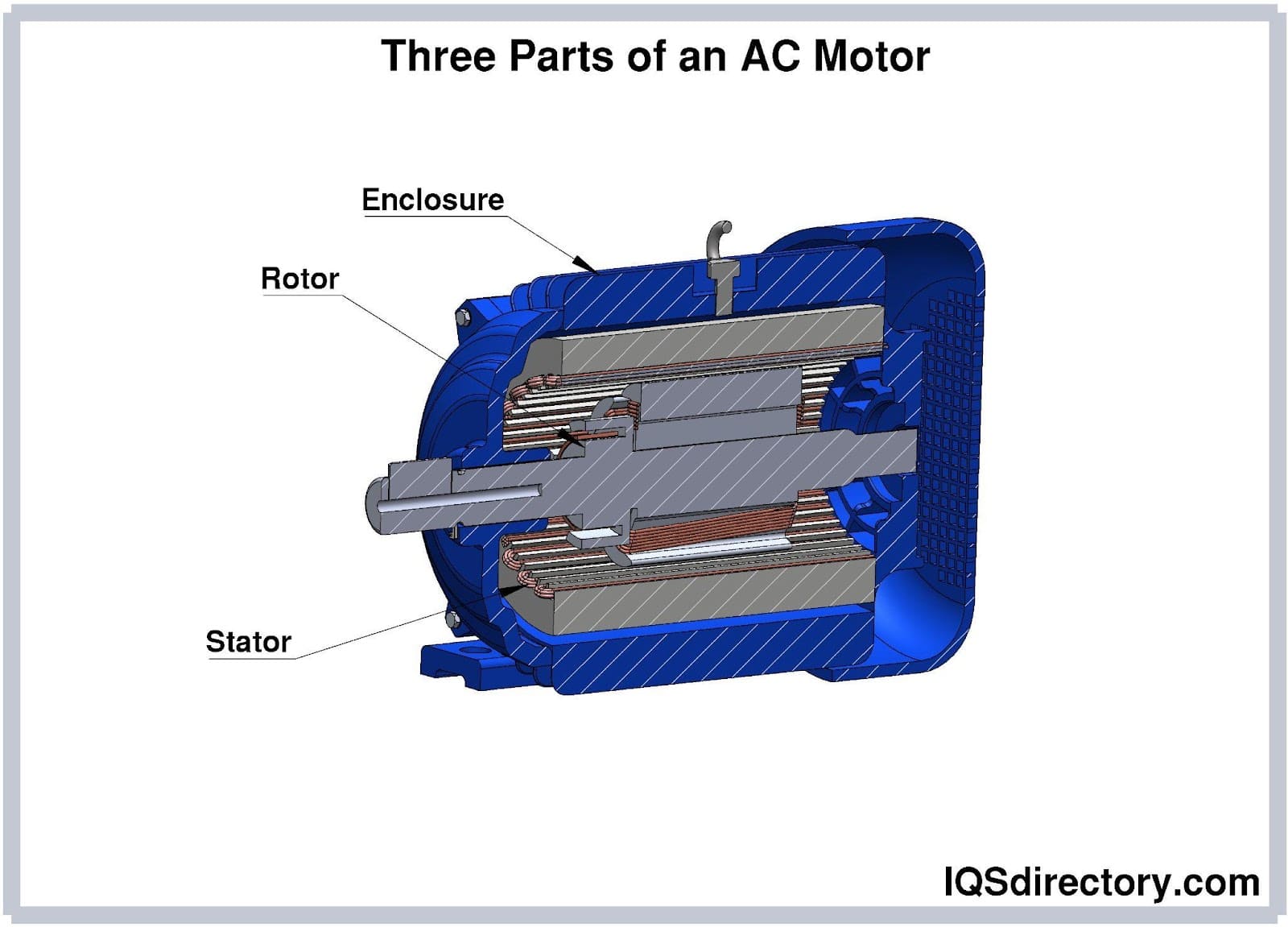
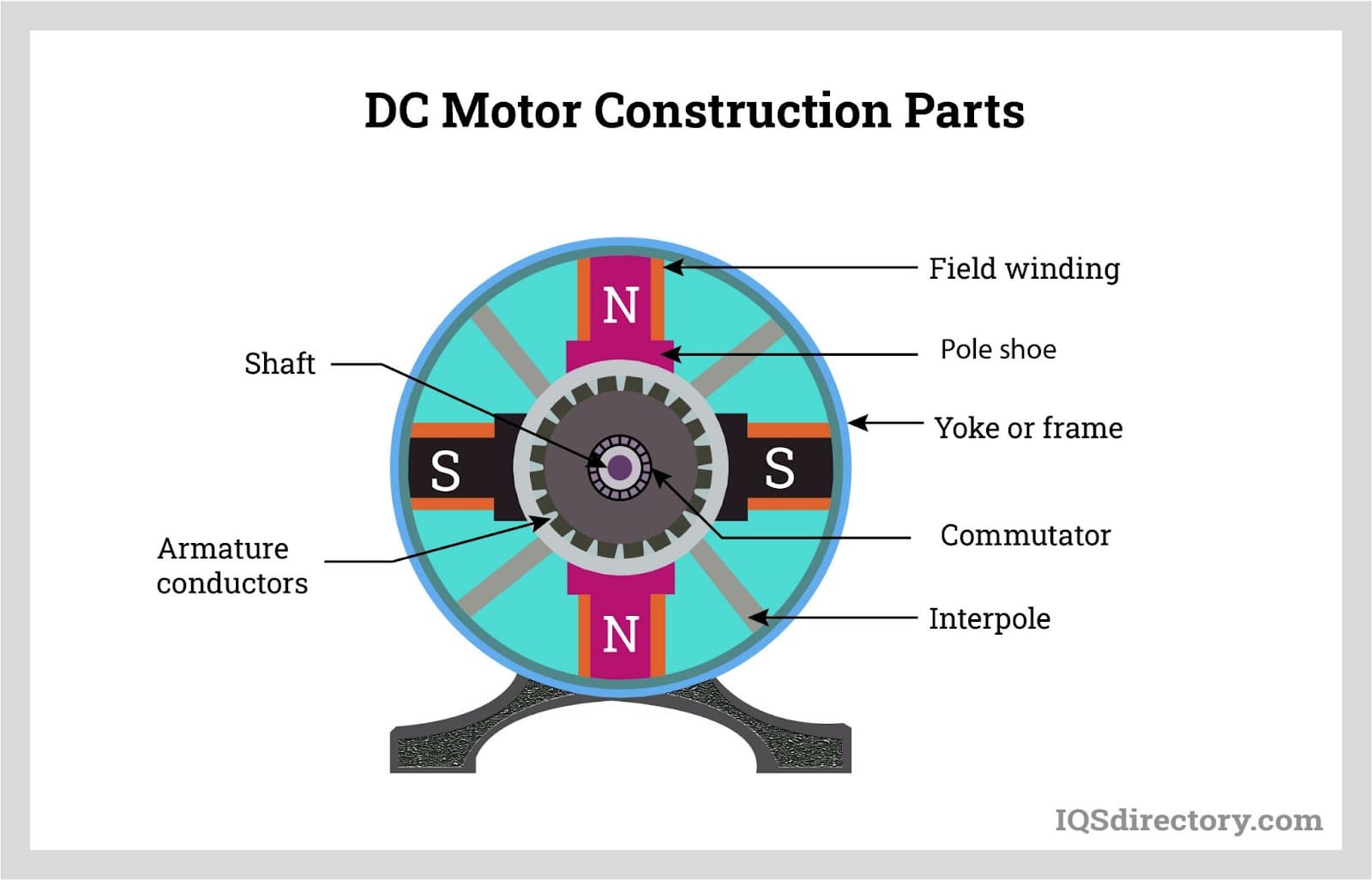
A universal motor's architecture is similar to that of a DC series motor, but it is specially designed to also handle AC power. Field poles are installed at the top of the stator, with weaved field coils attached to these poles. The stator and armature field circuits, as well as the complete magnetic route, are typically laminated to reduce eddy current losses, which are more prevalent when operating on AC supply.
The rotating armature is wound with straight or skewed slots, and the commutator features carbon brushes that rest upon it. In universal motors, commutation can be harsher on AC than on DC due to the alternating direction of induced currents in the armature coils. For this reason, high-resistance brushes are employed to minimize sparking and wear, increasing reliability and service life.
Traditional DC motors experience significant eddy current losses and heating of magnetic components when connected to AC sources, which reduces overall efficiency. Universal motors address these issues by using electromagnetic field windings instead of permanent magnets. This allows them to operate efficiently on both AC and DC power sources, making them a popular choice for dual-power or portable applications.

How Does a Universal Motor Work? Working Principle Explained
A universal motor can run on either a single-phase AC or a DC supply, providing unique flexibility for product designers and engineers. When supplied with DC power, a universal motor operates as a standard DC series motor. Electricity passing through the field winding generates an electromagnetic field, and the same current flows through the armature conductors. According to the Fleming left-hand rule, a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field experiences a mechanical force, or torque, which turns the rotor and produces rotational motion.
When powered by AC, the direction of the armature current and the magnetic field both reverse every half-cycle, but their relative direction remains unchanged. This ensures that the torque generated by the universal motor is always in the same direction, allowing consistent operation regardless of the power source. However, commutation is more challenging on AC, so universal motors are engineered with specific features (such as laminated cores and special brushes) to handle these demanding conditions.

Universal Motor Speed and Load Characteristics
Universal motors display performance characteristics similar to DC series motors, which makes them particularly valuable in applications demanding variable speed and high starting torque. When operating without a load (no-load condition), a universal motor can reach extremely high speeds—sometimes exceeding safe limits if not properly controlled. Under load, the speed decreases, but the motor can maintain strong torque output, making it ideal for tools and appliances where rapid acceleration and dynamic response are required.
To achieve specific operating speeds under varying loads, gear trains are often integrated with universal motors. This enables precise control in equipment such as power drills and blenders. Additionally, electronic speed controllers or variable resistors may be employed for finer speed regulation, depending on the application’s complexity and user requirements.

Applications of Universal Motors: Where Are They Used?
Universal motors are widely utilized across both consumer and industrial markets due to their ability to run on multiple power sources and deliver high-speed operation in a compact form factor. Common universal motor applications include:
- Portable Power Tools: Universal motors are extensively used in hand drills, jigsaws, grinders, sanders, and rotary tools, where their high starting torque and compact size are essential for user convenience and performance.
- Household Appliances: Devices such as vacuum cleaners, food processors, blenders, and domestic sewing machines rely on universal motors for efficient operation and variable speed control.
- Commercial Equipment: Floor polishers, carpet cleaners, and small industrial machines leverage universal motors for their reliability and adaptability to available power supplies.
- Fans and Blowers: Certain high-speed fans and blowers, especially portable or corded models, use universal motors for their rapid acceleration and portability.
- Hair Dryers and Personal Care Devices: Many high-speed hair dryers and other beauty appliances are powered by compact universal motors.
Are you seeking the best universal motor for your application? Read our section below on selecting reliable universal motor manufacturers and what to consider when specifying a universal motor for your next project.
Advantages of Universal Motors: Why Choose Them?
- Dual Power Compatibility: Universal motors can be powered by both AC and DC voltage sources, offering unmatched flexibility for portable and stationary devices.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to other fractional horsepower motors and AC induction motors, universal motors are less expensive to produce and maintain, making them attractive for high-volume, cost-sensitive applications.
- High-Speed Operation: The series-wound design of the field and armature windings allows universal motors to operate at extremely high speeds (from 3,600 RPM up to 25,000 RPM), fulfilling requirements in applications demanding rapid rotary motion.
- Compact and Lightweight: The small size and reduced weight of universal motors make them ideal for handheld and portable equipment, where ergonomics and ease of use are critical.
- Wide Power Ratings: Universal motors are available in a broad range of power ratings, from as low as 5 watts up to 500 watts, supporting both light-duty and heavy-duty tasks in residential, commercial, and light industrial settings.
- Simple Speed Control: Speed can be easily adjusted by varying the supply voltage or adding electronic speed controllers, enabling fine-tuned performance for different tasks.
Considering universal motors for your product design or manufacturing process? Evaluate their benefits against other electric motor types, such as shaded pole motors, induction motors, and permanent magnet motors, to determine the best fit for your needs.
Disadvantages and Limitations of Universal Motors
- Increased Noise Levels: Universal motors generate more noise than equivalent AC induction motors or brushless DC motors, especially at higher speeds. This can be a concern in noise-sensitive environments or premium consumer products.
- Vibration and Balance Issues: Due to the high-speed operation and mechanical structure, universal motors must be precisely balanced. Even minor imbalances can lead to strong vibrations, reducing performance and potentially causing mechanical failures or safety hazards.
- Limited Reversibility on AC: Reversing the direction of a universal motor is more complex on AC power than on DC, which may limit their suitability for bidirectional applications.
- No-Load Overspeed Risk: Universal motors, like DC series motors, can reach dangerously high speeds with no load attached, risking damage or failure. To prevent this, a fan or mechanical load is often attached to the rotor shaft, ensuring safer operation in all conditions.
- Brush and Commutator Maintenance: The use of carbon brushes and commutators introduces wear and tear, requiring periodic maintenance or replacement—unlike brushless or induction motors, which have lower maintenance needs.
- Lower Efficiency: Universal motors tend to have lower energy conversion efficiency compared to modern brushless DC or AC induction motors, particularly at partial loads or under variable speed conditions.
If you need quieter, more efficient, or maintenance-free operation, consider alternative technologies like brushless DC motors or induction motors. Not sure which motor is right for you? Consult our expert manufacturer directory for guidance.
How to Select the Right Universal Motor: Key Decision Factors
Choosing the optimal universal motor for your application involves evaluating several critical factors, including:
- Power and Speed Requirements: Determine the required horsepower or wattage, and the desired operating speed range, based on your application’s load profile and duty cycle.
- Voltage and Power Supply: Confirm the available supply voltage (AC or DC) and frequency to ensure compatibility with the universal motor’s specifications.
- Physical Size and Mounting: Assess the space constraints and mounting options within your equipment or product design.
- Thermal Management: Consider cooling requirements, especially for high-speed or continuous-duty applications, to prevent overheating.
- Noise and Vibration Tolerance: Evaluate acceptable noise and vibration levels for your application, balancing performance with user comfort.
- Maintenance and Lifespan: Factor in scheduled maintenance (such as brush replacement) and expected service life to minimize downtime and operational costs.
- Budget Constraints: Balance upfront costs with long-term performance and reliability to maximize return on investment.
Need help sizing or specifying a universal motor? Contact our listed universal motor suppliers for technical support, CAD drawings, and custom engineering solutions tailored to your project’s unique requirements.
Choosing the Correct Universal Motor Manufacturer
To ensure the best outcome when purchasing a universal motor, it's essential to compare several manufacturers and their capabilities. Start by exploring our comprehensive directory of universal motor manufacturers—each profile highlights areas of expertise, production capabilities, certifications, and customer support resources.
When evaluating universal motor manufacturers, consider:
- Experience and Track Record: Look for manufacturers with a history of supplying high-quality universal motors for your specific market or application.
- Customization Options: Does the manufacturer offer custom winding, shaft, mounting, or speed control options to suit your unique needs?
- Quality Assurance: Review certifications (such as ISO 9001), testing procedures, and warranty policies to ensure consistent product quality and support.
- Lead Times and Availability: Can the supplier meet your project timeline and volume requirements, including rapid prototyping or large-scale production?
- Technical Support: Access to engineering expertise, application guidance, and after-sales support is vital for successful integration and long-term performance.
- Pricing and Value: Compare quotes, minimum order quantities, and total cost of ownership to find the right balance between price and performance.
Use our directory’s business profile pages and patented website previewer to quickly evaluate each universal motor manufacturer. The built-in contact form allows you to reach out directly for more information or to request a quote. For maximum efficiency, use our simple RFQ (Request for Quote) form to contact multiple companies simultaneously.
Ready to take the next step? Request a quote from top universal motor manufacturers now, or keep reading to learn more about universal motor technology, trends, and best practices.
Frequently Asked Questions About Universal Motors
- What are the main differences between universal motors and AC induction motors?
Universal motors can operate on both AC and DC power, offer higher speeds, and are generally more compact. AC induction motors, by contrast, are more efficient, quieter, and require less maintenance, but lack the high-speed capability and dual-power flexibility of universal motors. - What industries most commonly use universal motors?
Universal motors are prevalent in consumer appliances (vacuum cleaners, blenders), power tools (drills, saws), commercial cleaning equipment, and certain medical and laboratory devices requiring high-speed operation. - How can I improve the lifespan of my universal motor?
Regularly inspect and replace brushes, avoid prolonged no-load operation, ensure proper ventilation, and observe recommended duty cycles to extend the service life of your universal motor. - Can universal motors be used in variable speed applications?
Yes, universal motors are easily controlled using variable resistors or electronic speed controllers, making them ideal for applications needing adjustable speed, such as mixers or power tools. - Are there any energy-efficient alternatives to universal motors?
Brushless DC motors (BLDC) and AC induction motors offer higher efficiency, quieter operation, and lower maintenance—consider these alternatives for fixed-speed or continuous-duty applications.
Universal Motors vs. Other Motor Types: A Comparative Overview
When selecting an electric motor, it’s crucial to compare universal motors with other common types to ensure the best match for your performance and application requirements:
- Universal Motors vs. Permanent Magnet Motors: Permanent magnet motors use rare earth or ceramic magnets, offering high efficiency and low maintenance but typically only operate on DC. Universal motors, by contrast, provide AC/DC versatility and high-speed capability.
- Universal Motors vs. Shaded Pole Motors: Shaded pole motors are simple and low-cost for low-torque applications, but lack the power and speed flexibility of universal motors.
- Universal Motors vs. Induction Motors: Induction motors excel in efficiency, longevity, and quiet operation, but are larger and cannot match the universal motor’s speed or dual-power operation.
- Universal Motors vs. Brushless Motors: Brushless motors offer quiet, maintenance-free operation, but at a higher initial cost and often with less speed flexibility than universal motors.
Still deciding which motor technology is right for your business? Contact our experts for personalized assistance or browse our technical resources for detailed motor comparisons and selection guides.
Universal Motor Trends, Innovations, and Future Outlook
With growing demand for energy efficiency, noise reduction, and smart appliance integration, universal motor technology continues to evolve. Recent advancements include:
- Improved Brush Materials: New carbon formulations reduce wear and extend maintenance intervals.
- Advanced Commutator Designs: Enhanced commutation for smoother operation and reduced electrical noise.
- Integrated Electronics: Built-in speed controllers and soft starters for better user experience and motor protection.
- Eco-Friendly Manufacturing: Adoption of recyclable materials and efficient production processes to minimize environmental impact.
As manufacturers work to meet stricter efficiency and environmental regulations, expect continued improvements in universal motor design, reliability, and performance. Stay up to date with the latest trends by following our industry news and product updates.
Explore More About Universal Motors
For more information, technical specifications, or a custom quote, reach out to our network of trusted universal motor suppliers today. Whether you’re an engineer, purchasing manager, or equipment designer, our directory and resources help you make informed decisions and source the best universal motors for your application.





 Air Cylinders
Air Cylinders Assembly Machinery
Assembly Machinery Ball Bearings
Ball Bearings Electric Motors
Electric Motors Fractional Horsepower Motors
Fractional Horsepower Motors Friction Materials
Friction Materials Linear Actuators
Linear Actuators Linear Bearings
Linear Bearings Linear Slides
Linear Slides Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services